THM write-up: Hacking with Powershell
6 minutes to read
Link: https://tryhackme.com/room/powershell
Greeting there, welcome to another tryhackme writeup. Today, we are going for the most fundamental room in THM which is the windows Powershell. (I’m feeling THM started to deep dive into Windows machine.) This post is written for those who stuck in the loop of PowerShell and don’t rely on this walkthrough so much, somehow you need to learn :). In addition, the command and the script within the walkthrough might not be clean or optimize.
Task 2: The most useful PowerShell command
Every time, even you are a Linux user. You should know help command is the most useful command in all sorts of the shell. How about the Powershell? Get-Help
Task 3: Basic Powershell
Make sure you read the entire description of the challenge, that is informative.
Task 3-1: Location of a file
This task required the user to search for a .txt file. To do this, we need the following Powershell command
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Include *.txt -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Let me explain the flags:
- -Path: Path we are looking for. C;\ for the entire disk
- -Include: The name of the file. In this case, I put a wildcard for the text file
- -File: File only
- -Recurse: Recursive search
- -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue: Ignore error
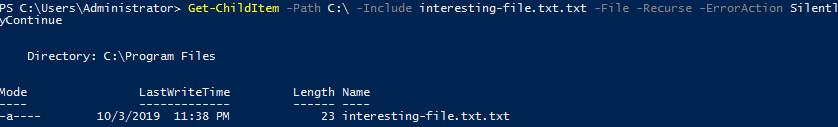
The text file is located in C:\Program Files
Task 3-2: Read the file
To read the content of a file, you need the following command
Get-Content -Path 'C:\Program Files\interesting-file.txt.txt'

Task 3-3: Count the cmdlets
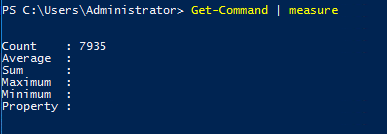
For the hardcore, you can list all cmdlets and count by yourself. If you are lazy just like me, pipe a measure command.
Get-command | measure
Task 3-4: MD5 hash
This is easy, enter the following command to get the checksum of the file.
Get-FileHash 'C:\Program Files\interesting-file.txt.txt' -Algorithm MD5

Task 3-5: Get current working directory
Just like DIR in windows and ls in Linux. Powershell uses Get-Location to list the file and directory.
Task 3-6: Check the existence of a file
Use Get-Location to verify whether the file is inside the system or not.
Get-Location "C:\Users\Administrator\Documents\Passwords"
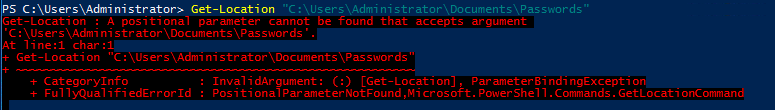
The answer is Nay.
Task 3-7: Make a web request
Check this link, it explains everything.
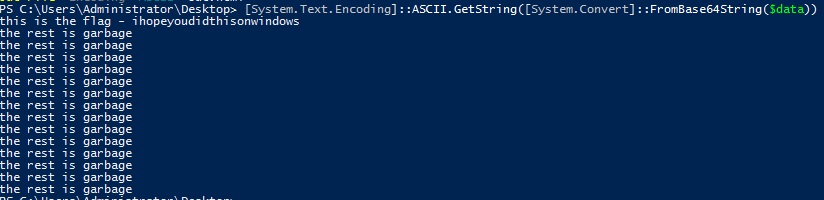
Task 3-8: Decode base64
You can cheat yourself using an online tool but it is meaningless. To perform a base64 decode via Powershell, use the following command.
PS> $data = Get-Content 'b64.txt'
PS>[System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String($data)) | Out-File -Encoding "ASCII" out.html
Task 4: Enumeration
We are going to do some recon using Powershell.
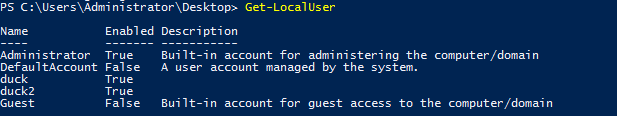
Task 4-1: Who is inside the machine
To list all users inside the machine, you need the following command.
Get-LocalUser
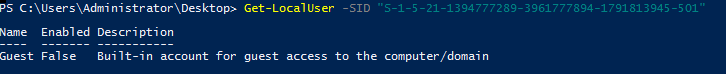
Task 4-2: The user SID
Just add -SID flag on Get-LocalUser.
Get-LocalUser -SID "S-1-5-21-1394777289-3961777894-1791813945-501"
Task 4-3: User with NoPassword
4 user, that all.
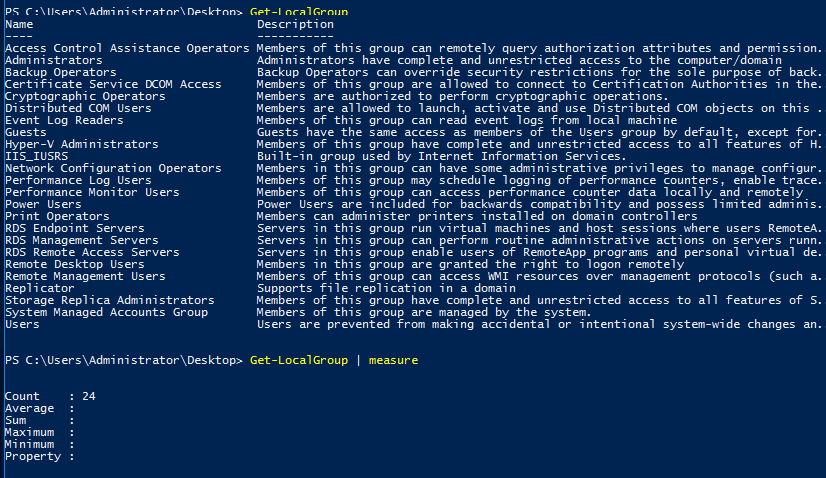
Task 4-4: Number of the local groups
Similar to the previous task on listing the number of cmdlets, pipe the measure command after Get-LocalGroup.
Get-LocalGroup | measure
Task 4-5: Get IP address info
well, Get-NetIPAddress
Task 4-6: Listening port
Get-NetTCPconnection filtered with -state listen flag.
Get-NetTCPconnection -State Listen
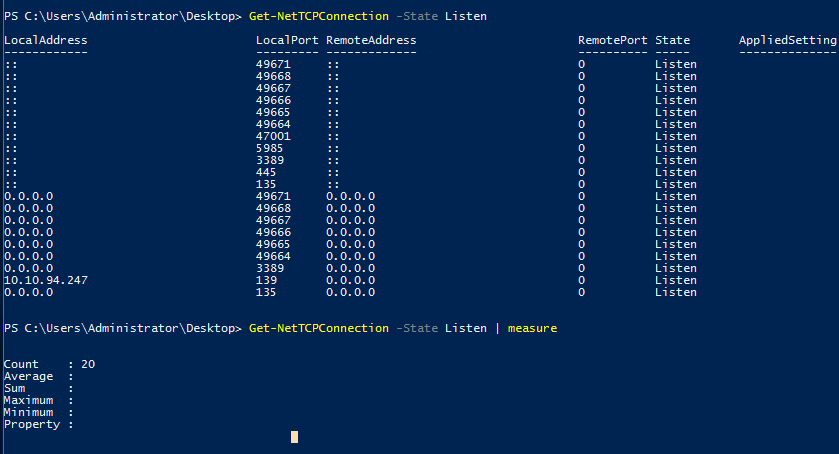
Task 4-7: Remote address for Port 445
Still using the Get-NetTCPconnection but with -State and -LocalPort flags.
Get-NetTCPconnection -State Listen -LocalPort 445

Task 4-8: Number of installed patch
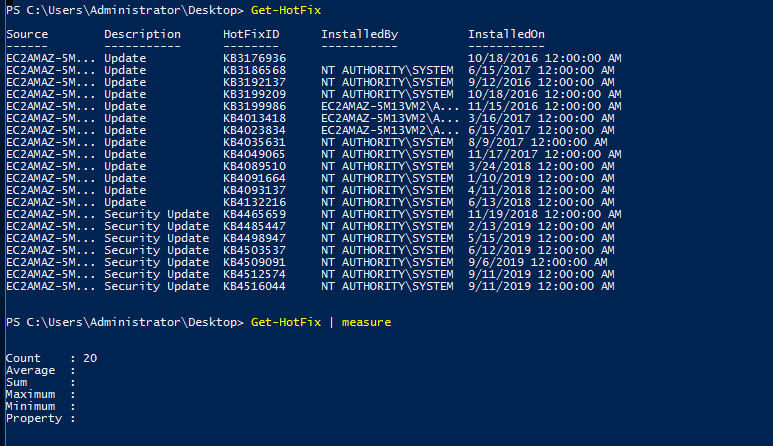
You need Get-hotfix command
Get hot-fix | measure
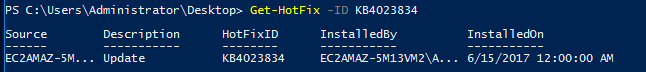
Task 4-9: Patching date
To look for a specific path ID, punch in the following command.
Get-HoxFix -ID KB4023834
Task 4-10: Read a backup file
This task is a little bit tricky. The backup file always ended up with .bak but not this one. That is why I added up wild card back and fro the file searching command.
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\ -Include *.bak* -File -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
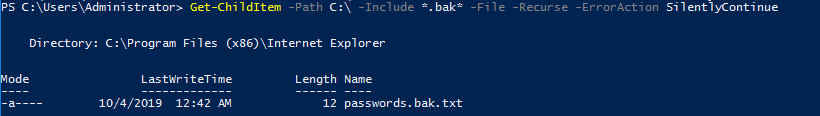
See, that is a text file.
Task 4-11: The API key
You are required to read all the files line by line. I’m thinking of grep command. The alternative of Powershell to grep is.
Get-ChildItem C:\* -recurse | Select-String -pattern API_KEY
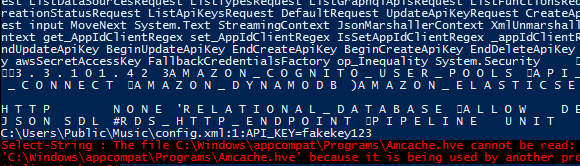
Huh, where is it?
Task 4-12: List running process
is Get-Process
Task 4-13: Find the scheduled task
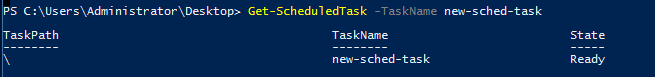
To find a specific scheduled task, just input the following command.
Get-Scheduledtask -TaskName new-sched-task
Task 4-14: The owner of C:\
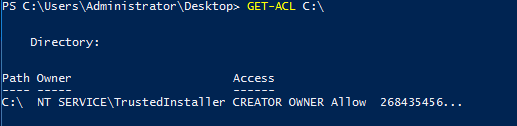
GET-ACL is the answer you need.
Get-Acl C:\
Task 5: Basic scripting
Time for some hands-on. Actually we can finish all the tasks with one command line but for the sake of the challenge, I’m going to write a simple script. Seriously, don’t read the files.
Task 5-1: Locate the file with password
Launch your ISE, write the following script and run it.
$path = 'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\emails\*'
$magic_word = 'password'
$exec = Get-ChildItem $path -recurse | Select-String -pattern $magic_word
echo $exec
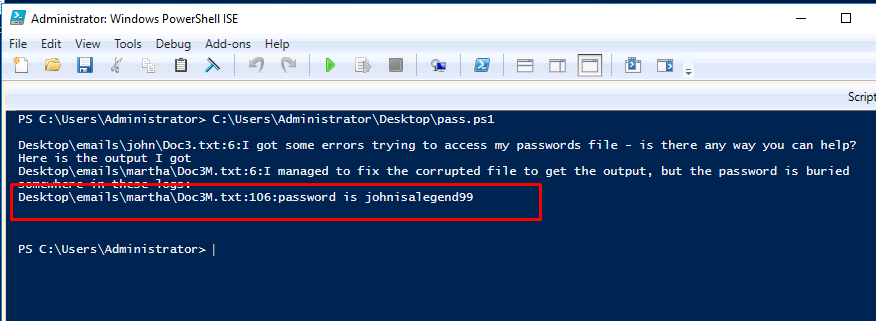
Easy huh.
Task 5-2: The password
The answer can be found on task 5-1.
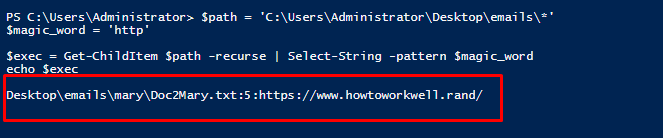
Task 5-3: File with link
Just change the $magicword variable to “HTTP” and you should get the answer.
Task 6-1: Intermediate scripting
11
Conclusion
That’s all for the Powershell challenge. It doesn’t matter the command is upper or lower case, this is Windows OS. Until next time ;)
tags: tryhackme - recon - windows - powershellThanks for reading. Follow my twitter for latest update
If you like this post, consider a small donation. Much appreciated. :)