CyberEDU write-up: Entry
11 minutes to readWelcome and welcome back to another CTF writeup. This is my third new series of the week. Today we are going to walk through some of the entry-level challenges on CyberEDU. For your information, the site is hosted by volunteers from the Cyber Security Research Center from Romania (CCSIR) and it is currently free for all. Since CyberEDU is still on a beta version (while writing this post), you might encounter bugs while accessing some of the features on the site. Without further ado, let’s get started.
- [D-CTF 2019] base (10 points)
- [ECSC 2019] Out of the image (10 points)
- [ECSC 2019] mathematics (10 points)
- [D-CTF 2019] address (10 points)
- [D-CTF 2019] password (10 points)
- [D-CTF 2019] mountain (10 points)
- [D-CTF 2019] inception (10 points)
- [D-CTF 2019] cross-or-zero (10 points)
- [D-CTF 2019] corrupt-file (10 points)
- [ECSC 2019] xo.rar (50 points) - pending
- [ECSC 2019] ping-pong (10 points) - pending
1) [D-CTF 2019] base (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55e16d00-7f21-11ea-99d5-e91c3e9dcacc/
This challenge required the user to complete all three tasks within a limited time frame. Those three tasks are
- Convert decimal to hex
- Convert hex to ASCII
- Convert Octal to ASCII
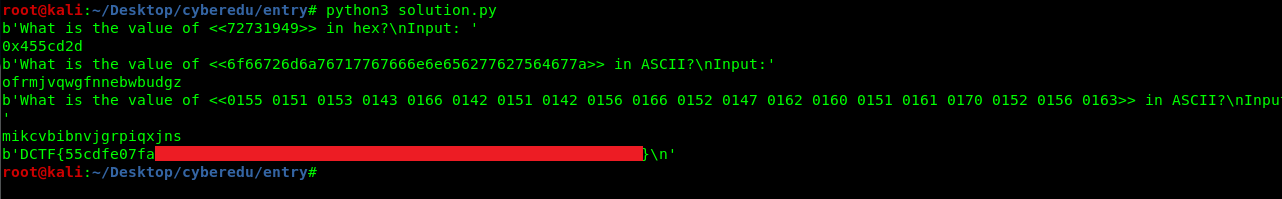
The simplest way is to create a simple python script with a socket enabled. Please note that the script is not optimized and it is intended for the beginner. If you have a better script, you are welcome to provide one. Also, change the host address and port if necessary.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import socket
#Change it!
HOST = '35.234.92.174'
PORT = 31030
count = 0
#connect to host and port
sock = socket.socket()
sock.connect((HOST, PORT))
#There are a total of 3 challenges
while count < 3:
# receive the response, do a flush out if 'input' string is not showing on the response
response = sock.recv(4096)
str_response = repr(response)
if (str_response.find("Input") == -1):
flush = sock.recv(4096)
#Extract the data by finding << and >>
special1 = str_response.find('<') + 2
special2 = str_response.find('>')
if (count == 0):
# Challenge 1: Decimal to hex
response_trim = str(hex(int(str_response[special1:special2])))
elif (count == 1):
#challenge 2: hex to ascii
response_trim = bytes.fromhex(str_response[special1:special2]).decode("utf-8")
elif (count == 2):
##challenge 3: octal to ascii
response_trim = ""
response_list = str_response[special1:special2].split(' ')
for i in response_list:
data = chr(int(i, 8))
response_trim = response_trim + data
response_process = response_trim + '\n'
print(response)
print(response_trim)
sock.send(bytes(response_process, 'utf8'))
count = count + 1
# Receive Flag
response = sock.recv(4096)
print(response)
sock.close()
2) [ECSC 2019] Out of the image (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55d041e0-7f21-11ea-be5e-c9459c7a94df
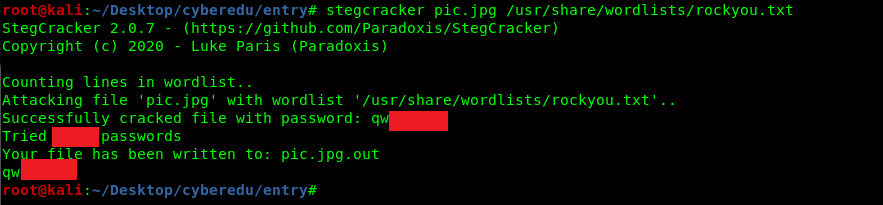
The task can be easily solved using stegcracker with rockyou.txt as the wordlist.
stegcracker pic.jpg /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
3) [ECSC 2019] mathematics (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55cf2ac0-7f21-11ea-9dac-19639bd852f1
This is my favorite task as it involves with reverse engineering. I’m using ida to complete this task. First of all, let’s analyze the branch that lead us to the flag.
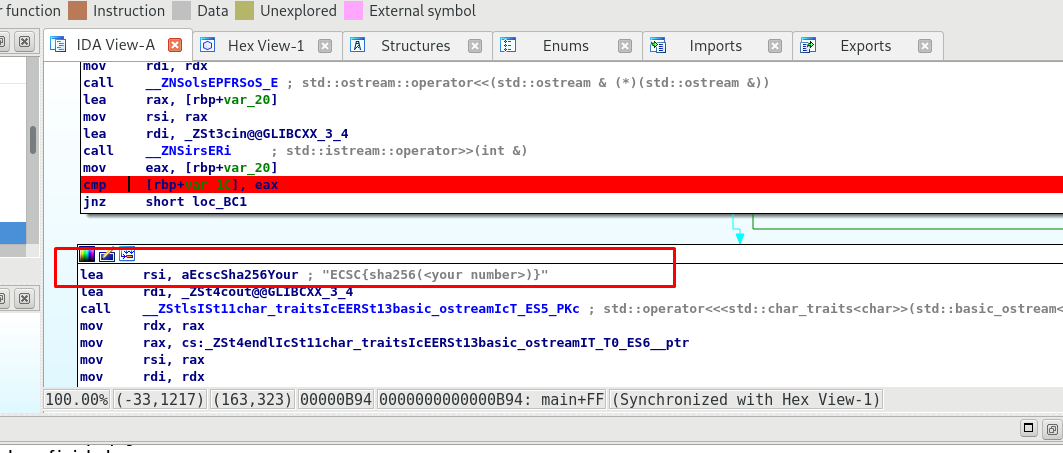
The branch with ECSC{…} is the branch we need. In order to get into the branch, [rbp+var_1C ] must be equal to the eax register. Hence, we have to put a break-point on the cmp instruction and see what parameter that lead us into it.
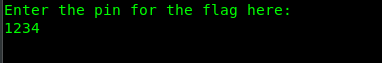
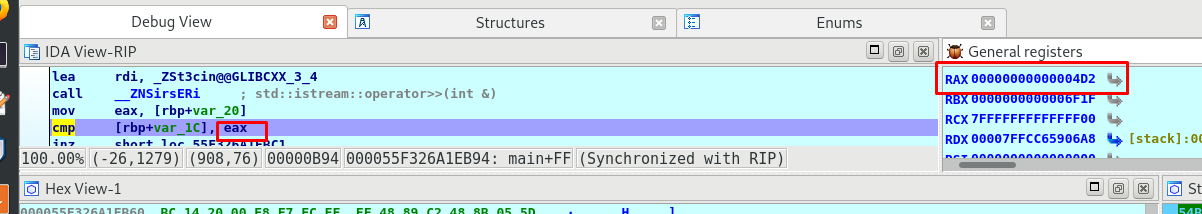
Like I expected, the eax register holds the dummy input. For your information, the hex of the decimal number, 1234 is 0x4D2. Our goal right here is to find the value that saved on the rbp+var_1C stack
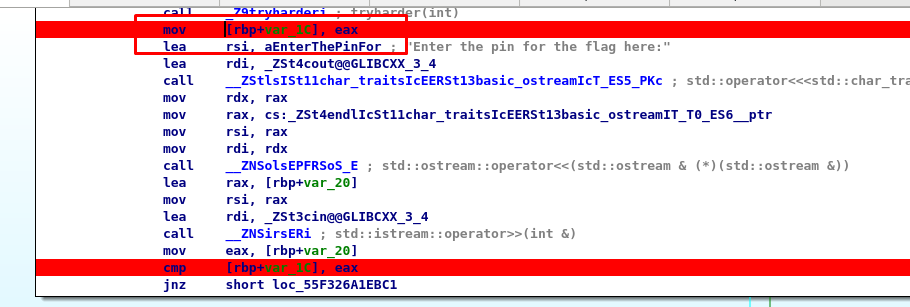
By looking at the instruction on the further up, we knew that the mov instruction contain the answer we need.
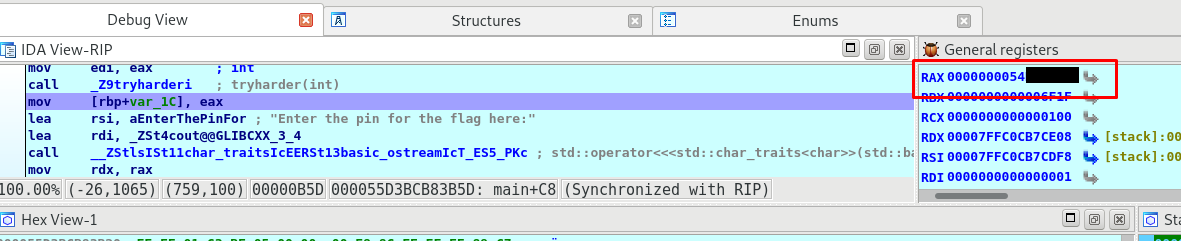
That’s it, convert the hex on register eax into decimal number. After that, input the decimal pin into the executable and you should get the answer.
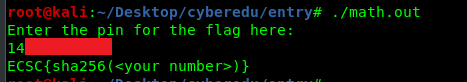
Remember to encode the number into sha256 before submitting the flag.
4) [D-CTF 2019] address (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55df47c0-7f21-11ea-b35d-457ba9a78ba1
This is a web-based CTF challenge. Let’s take a look on the page and the source code.
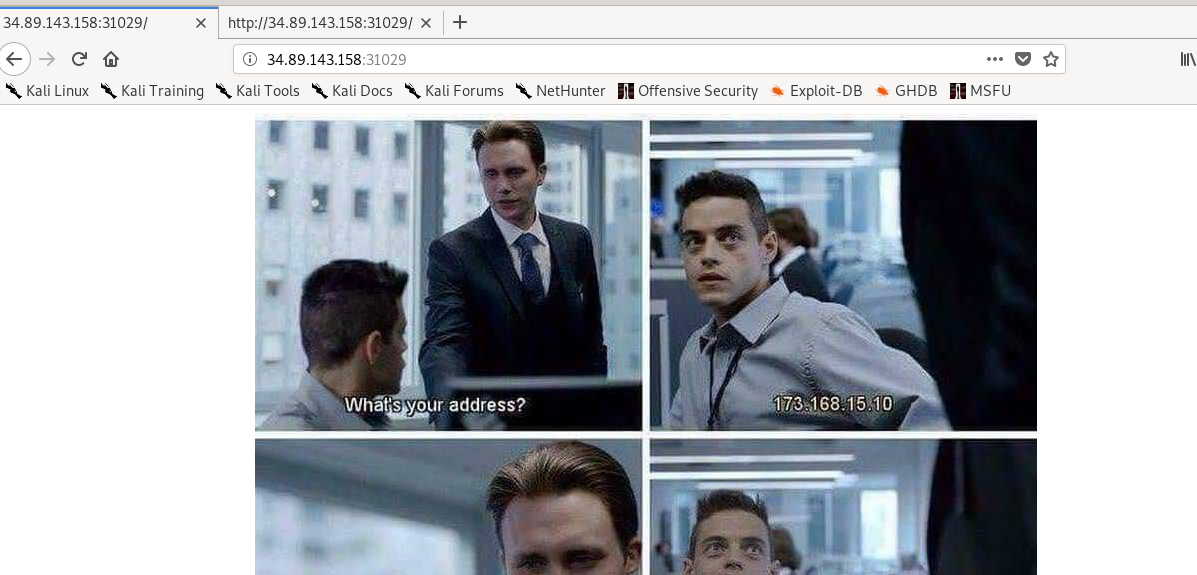
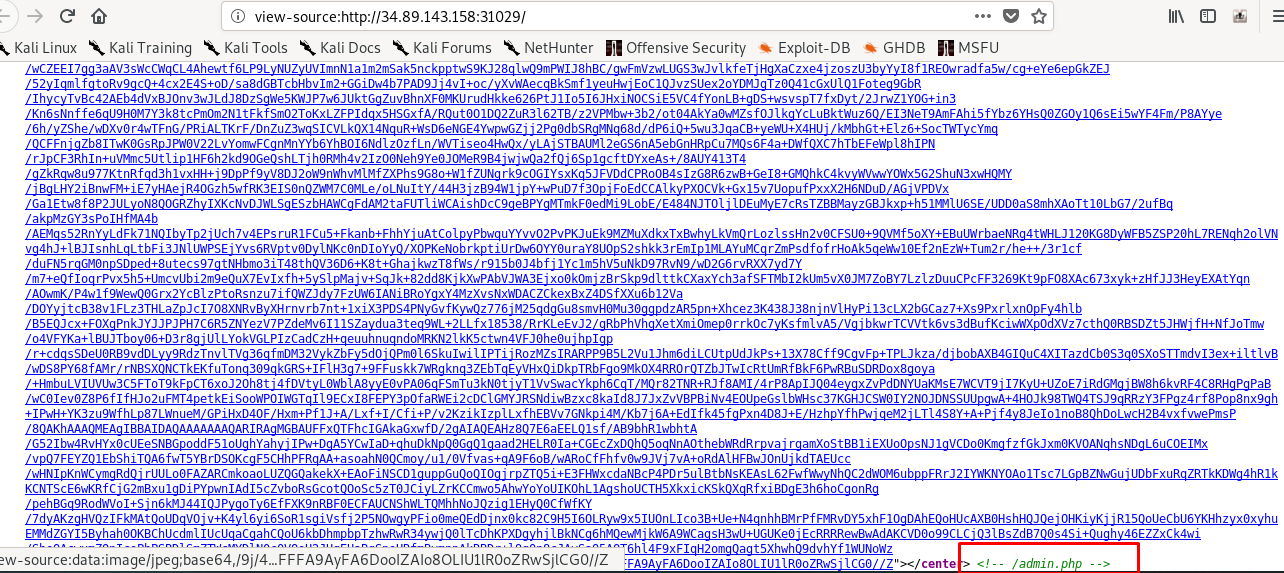
Hint on the bottom of the source code, admin.php.
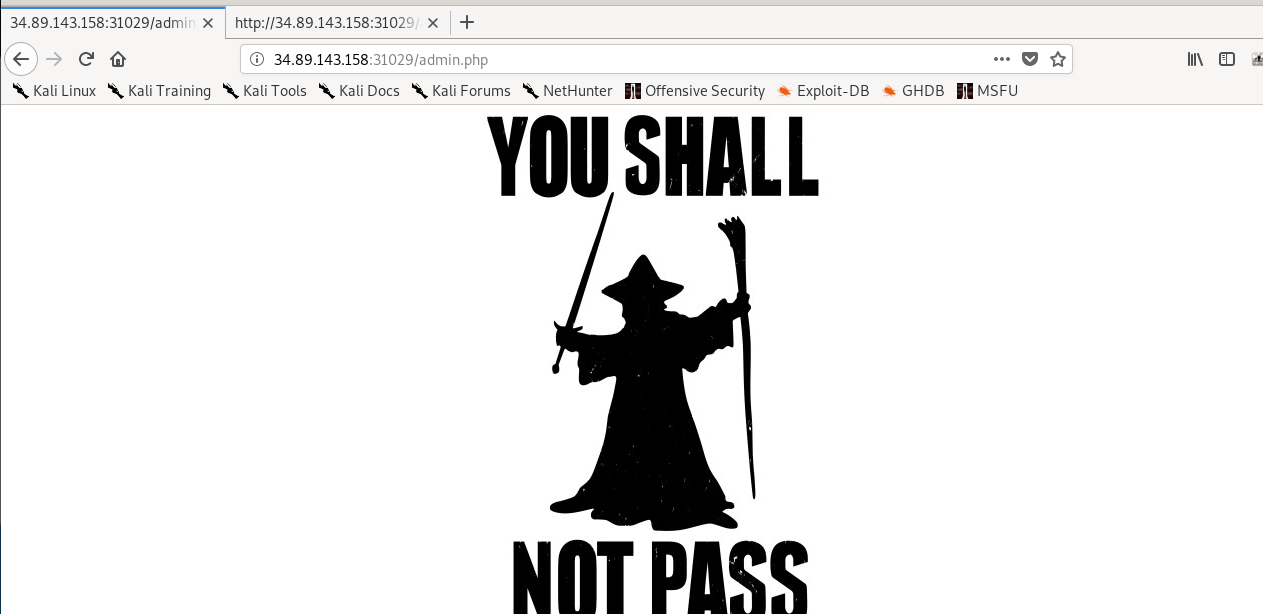

Two meme materials on the same site, you got me there. By the way, it seems that only the local able to bypass this page. Guess what, we can spoof our way in using X-forward-for header. There are two ways to solve the task
A) Curl command
Simply input the following command and you should get the flag. Please change the assigned IP and port.
curl -XGET http://<IP:port>/admin.php -H 'X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1'

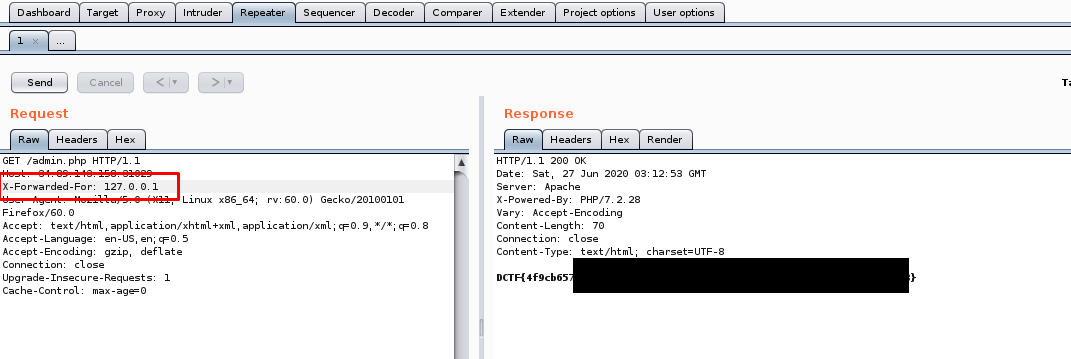
B) Burp suite
You can use repeater mode in burp suite by adding an extra request header (X-Forwarded-For: 127.0.0.1)
5) [D-CTF 2019] password (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55c17930-7f21-11ea-a774-e3c685b9cb45
First of all, de-compile the executable python file (.pyc) into a normal python file (.py) using the uncomplye6
uncompyle6 chall.pyc
Read the python file.
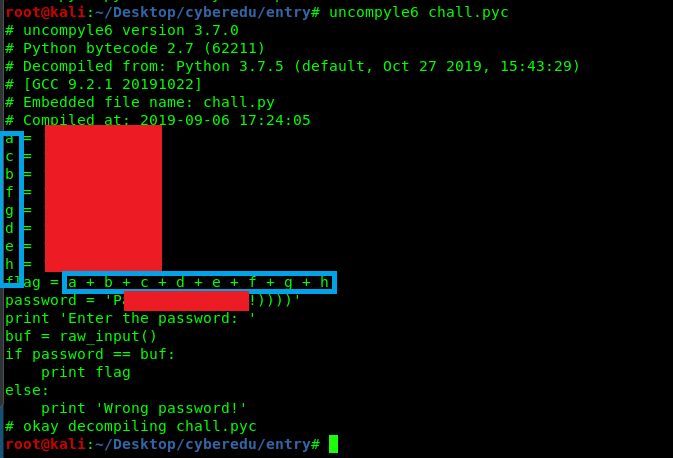
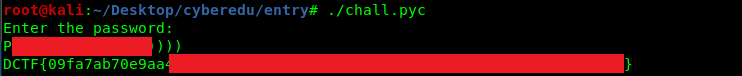
You can directly piece up the flag on the screen but the position of the flag is disoriented. The best way to capture the flag is by running the executable with the password.
6) [D-CTF 2019] mountain (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55c03860-7f21-11ea-b4d3-2925e2b578ee
The task can be solved by using stegoveritas or photo editor software such as Adobe Lightroom. The flag is located at the top left of the picture.

However, at the end of the flag, there are 3 letters hardly to be seen by the naked eye. After using my photo editing skill, the 3 letters are ‘6ff’

7) [D-CTF 2019] inception (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55bee840-7f21-11ea-9848-99f815545ba1
This is another Stego challenge that can be solved by using binwalk.
binwalk --dd='.*' chall.jpeg
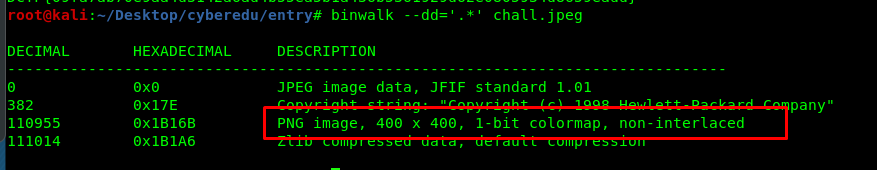
There is a hidden PNG image file inside the JPEG.
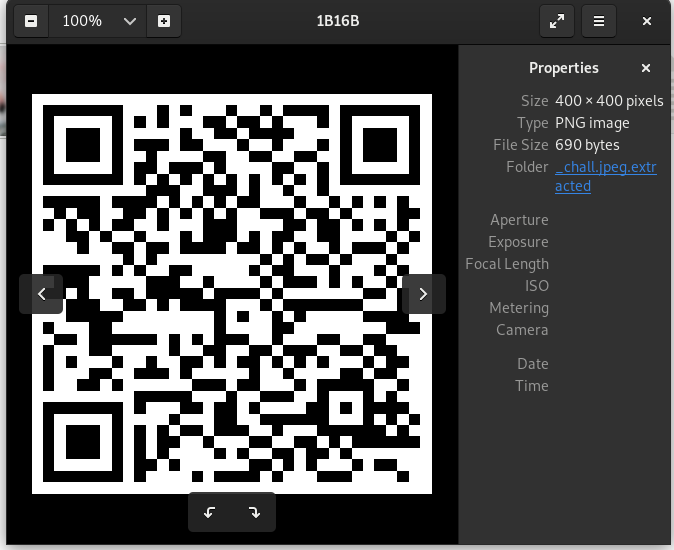
Decode the QR using online tool.

8) [D-CTF 2019] cross-or-zero (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55bdb360-7f21-11ea-af3b-91f50ec4f0b1
Don’t let the downloaded script scare you off. What we need inside the script is the base64 encoded text and the rough idea of the script, that’s all. The entire idea of the script is
Encoded text = base64.encode(flag ^ key)
Simple huh. Since we have the encoded text, the next thing we need to do is finding the key. Given the first four characters of the flag is ‘DCTF’ or 0x44 0x43 0x54 0x46 in hex. On the other hand, the first four-byte of the decoded base64 text is 0x74 0x73 0x64 0x76. And now, we can retrieve the key, given that
key = base64.decode(Encoded text) ^ flag
Decoded text: 0x74 0x73 0x64 0x76
Flag: 0x44 0x43 0x54 0x46
------------------------XOR--------------------------
Key: 0x30 0x30 0x30 0x30
The key is 2-byte repetitive. We can know draft a python script to retrieve the flag.
import base64
#Encode text and key
enc64 = "dHNkdktTAVUHAABUA1VWVgIHBAlSBAFTBAMFUwECAgcAAAFWAFUFCFMACFFUAwQAVgBSBwQJBVZTAFYGCQYHVQABB1IJTQ=="
key = 0x30
flag = ''
#decode the base64
dec64 = base64.b64decode(enc64).hex()
print("Decoded text in hex: " + dec64 + "\n")
# XOR the decoded text with the key
for i in range(0, len(dec64), 2):
x = int(dec64[i:i+2],16)
flag = flag + chr(x ^ key)
print("Flag: " + flag)

9) [D-CTF 2019] corrupt-file (10 points)
Link: https://cyberedu.ro/app/challenges/55bc94c0-7f21-11ea-9daa-a3bc85c91e3d/
Download and extract the .docx file. For your information, this is not a .docx file. By using ‘file’ command, it was actually a .xz file.

Rename the file into .xz and decompress it.
mv flag.docx flag.xz
unxz flag.xz

Conclusion
That’s all for the CyberEDU entry level write-up. Until next time ;)
tags: backdoor - ctfThanks for reading. Follow my twitter for latest update
If you like this post, consider a small donation. Much appreciated. :)